Capital budgets (like all other budgets) are internal documents used for planning. These reports are not required to be disclosed to the public, and they are mainly used to support management’s strategic decision making. Though companies are not required to prepare capital budgets, they are an integral part in planning and the long-term success of companies.
Ask Any Financial Question
- During capital budgeting, this analysis is used to understand how the variability in the output of a model (or system) can be apportioned, qualitatively or quantitatively, to different sources of variation.
- Decision makers consider these factors and select the optimal mix of projects that maximizes return while staying within the firm’s risk tolerance levels.
- For example, acquiring a new business to enter a new market or starting a different product or service is a strategic level investment decision which requires initiative from senior management.
The payback period is calculated by taking the total cost of a given project and dividing it by the amount of cash it is expected to generate each year. It offers a framework for evaluating the profitability and financial implications of potential investments. For instance, capital budgeting techniques like Net Present Value (NPV) or Internal Rate of Return (IRR) can help gauge the profitability of a proposed project. This is crucial because such investments often entail significant financial commitments.
Operating Income: Understanding its Significance in Business Finance
This method provides the ratio of the present value of future cash inflows to the initial investment. A Profitability Index that presents a value lower than 1.0 is indicative of lower cash inflows than the initial cost of investment. Aligned with this, a profitability index great than 1.0 presents better cash inflows and therefore, the project will be accepted. The capital budget is used by management to plan expenditures on fixed assets.
Avoidance Analysis
Since there is no ‘one-size-fits-all’ factor, there is no defined technique for selecting a project. Every business has diverse requirements and therefore, the approval over a project comes based on the objectives of the organization. It mainly consists of selecting all criteria necessary for judging the need for a proposal. In selecting a project based on the Payback period, we need to check for the inflows each year and which year the inflows cover the outflow. The net present value for both the projects is very close, and therefore taking a decision here is very difficult.
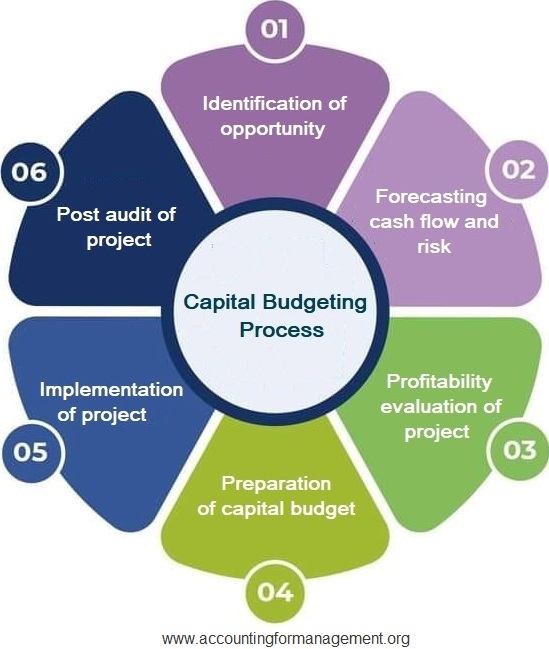
The purpose of capital budgeting is to make long-term investment decisions about whether particular projects will result in sustainable growth and provide the expected returns. Under avoidance analysis, determine whether increased maintenance can be used to prolong the life of existing assets, rather than investing in replacement assets. This analysis view your paychecks and w can substantially reduce a company’s total investment in fixed assets. This is an especially useful option when the incremental maintenance expenditure is not significant, such as when there is no need for a major equipment overhaul. Use this capital budgeting technique to find the discount rate that’ll bring a project’s net present value to zero.
Build your skills with a risk-free demo account.
Capital budgets helps to determine the type and quantity of projects a company invests in. When a company commits to CSR, it opts to finance projects that contribute positively to society alongside those that ensure profit-making. For instance, a corporation may allocate funds to support renewable energy or engage in ethical sourcing, channeling investments in a way that reflects its dedication to CSR. The role of capital budgeting in corporate social responsibility (CSR) has increasingly become vital in contemporary business concepts. This relationship is defined by the keen focus on how organizations incorporate social and environmental factors while deciding on investment proposals. The payback period approach calculates the time within which the initial investment would be recovered.
Here, The IRR of Project A is 7.9% which is above the Threshold Rate of Return (We assume it is 7% in this case.) So, the company will accept the project. However, if the Threshold Rate of Return would be 10%, then it would be rejected as the IRR would be lower. In that case, the company will choose Project B which shows a higher IRR as compared to the Threshold Rate of Return. This calculator uses the Effective Annual Rate (EAR) to accurately compute the interest rate per payment period when your payment frequency differs from the interest compounding frequency.
By incorporating such aspects into their capital budgeting process, organizations can actively pursue their CSR goals. In contrast, scenario analysis examines the impact of a change in a set of variables on a capital budgeting decision. Capital budgeting is a planning and decision-making process used to identify and evaluate opportunities to invest in long-term physical assets, and to allocate capital funds to selected investments. In taking on a project, the company involves itself in a financial commitment and does so on a long-term basis, which may affect future projects.
